Bleeding Control Basics
What is Bleeding Control?
Bleeding control refers to the techniques used to stop or reduce blood loss from an injury. Timely and effective bleeding control can save lives and prevent shock.
Types of Bleeding
- Arterial Bleeding: Bright red, spurting blood from an artery, typically life-threatening.
- Venous Bleeding: Dark red, steady blood flow from a vein, can be serious but is often less urgent.
- Capillary Bleeding: Slow, oozing blood from small blood vessels, usually minor and manageable.
Importance of Bleeding Control
Effective bleeding control is crucial to prevent excessive blood loss, reduce the risk of shock, and promote better outcomes for the injured person.
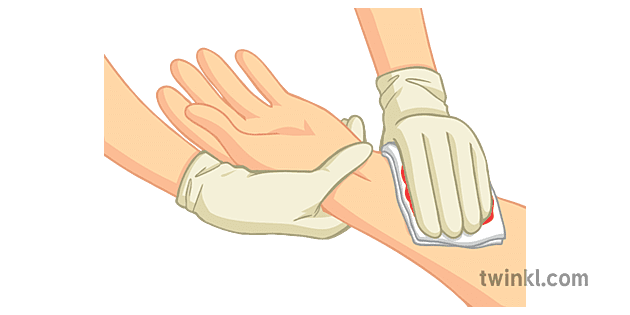
First Aid for Bleeding Control
Steps for Minor Bleeding
- Wash your hands and wear gloves if available.
- Apply direct pressure to the wound using a clean cloth or bandage.
- Keep applying pressure until the bleeding stops.
Steps for Severe Bleeding
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Apply firm pressure directly on the wound with a clean cloth or bandage.
- If blood soaks through, do not remove the original cloth; instead, add more layers on top.
- Elevate the injured area above the level of the heart if possible.
Steps for Arterial Bleeding
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Apply direct pressure to the wound.
- If bleeding continues, use a tourniquet above the wound site if trained to do so.
- Monitor the person's condition until help arrives.
Conclusion
Knowing how to control bleeding can significantly impact the outcome in emergency situations. Always prioritize safety and call for help when necessary.